STARTING BALL AND FINAL DISH
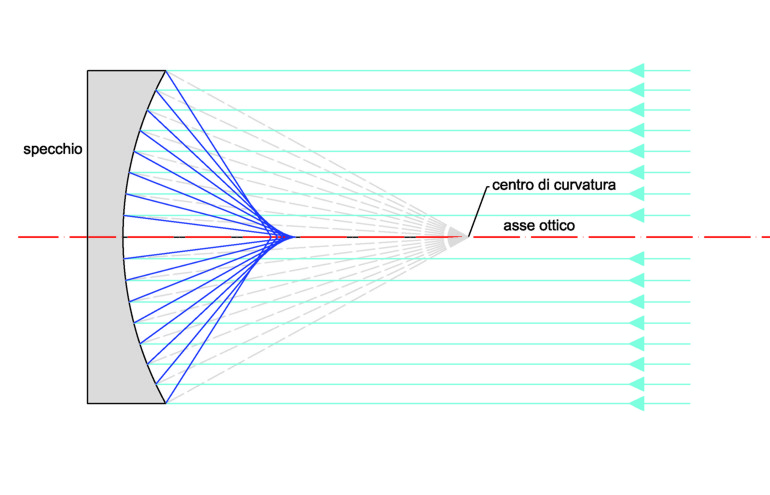
the reflection of light emanating from infinity on a spherical surface does not generate, as it is known, a single focus point, but rather a figure that “caustic reflection” which identifies the rotation surface where they concentrate the reflections of a point source .
As you can be seen in Figure 1 obtained by a simple geometric construction, the marginal rays converge at a point closer to the mirror with respect to the central ones.
The problem of Grattavetro is to make sure that all the rays coming from the mirror reflections converge in the vicinity of one and the same point within certain tolerance criteria, ie it is to modify the reflective surface to be spherical parabolic which, For definition, converges all the reflected rays at a single point which coincides with the focus of the parabola.
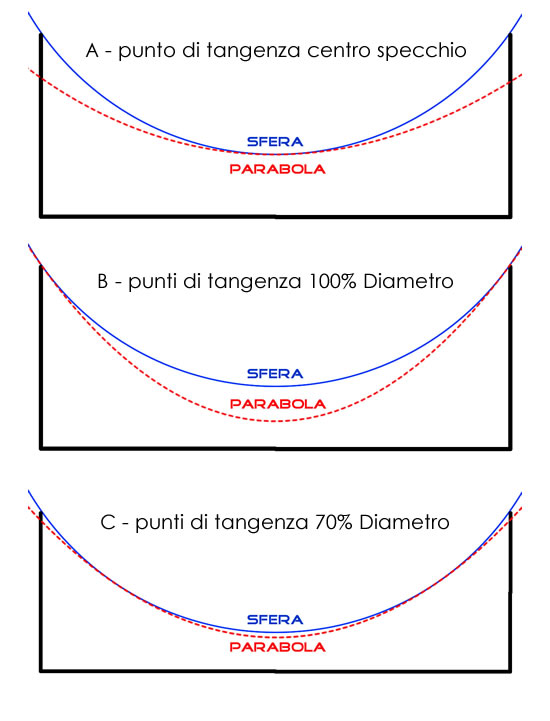
Keeping aside the theoretical aspects, we see in practice how many and what approaches can be used to build the parable referring to the figure 2:
A – “lengthen” peripheral reflections; It is to say that we leave the center as it is and we move to the suburbs on decreasing gradually the curvature of the mirror to make sure that the most distant reflections converge, just enough to make them coincide with the central ones.
B – “We shorten” central reflections: It is tantamount to saying that, starting from the edge and we move gradually towards the center will increase the curvature of the mirror in such a way that the reflections of the central zones converge closer, just enough to make them coincide with those devices.
-– “We shorten” central and reflections “lengthen” peripheral reflections taking as a reference a median point on the optical axis within the caustic where to coincide all the reflections.
THE METHOD“70%”
we start from the method of FIG C. 2 , which is generally the most used and known. In practice, it designs and builds the parable by aligning the two figures (initial and final parable ball ) at an intermediate point located at 70% the diameter.
This choice is made essentially for two reasons:
- for a machining economy, as you can see from the comparison with other methods, this configuration ensures the minimum removal of material to arrive at the final figure
- races W with full diameter generate on its surface this type of effect, ie, a deepening of the center and a lowering of the periphery leaving unchanged the curvature in the area to 70 % the diameter.
Contraindications:
while it is fast and simple application, the limit of this method is in the fact that an excessive peripheral sag is difficult to fix ( the grattavetro can only remove material from the mirror, while in this case would add ! ) to the point that it is better to go directly to the sphere to start again with a new approach to the parable.
If in the case of medium to long focal lengths ( F5-F6 )may not be a problem as the deviation of the parable from the sphere of origin is very small and can be reached relatively quickly, in the case of short focal lengths, equal to or less F4, the speech becomes more complicated since the material to be removed and the construction work begin to take important values. A return to the sphere of these processes is highly desirable.
THE METHOD“100%”
The sphere and the parabola are tangent in the edge of the mirror. Since the choice of the points of tangency of the parable about the reference sphere is arbitrary, we can decide to match the two curves in the ends of the mirror edge, as shown in Figure 1B
pros and cons
This processing method is what interests us more closely to the parabolic generation “pushed” with a focal length between F2 and F4. It fits very well to the use of sub-diameter, also you do not run the risk of generating edge retorted ( May May dire… ) o in “flatten” the periphery of the mirror, because the working process that we will lead us to dig more approaching the center, while the end of the edge will never be affected by the processing, we hardly need a return to the sphere of origin, as we shall see this combined approach with the use of sub-diameter it is much more “flexible” and tolerant of machining errors, we will always ( almost ) the possibility of increasing or decreasing back to our liking the curvature of the individual zones until it reaches the desired figure.
The price to pay for this increased security and reliability of the technique and to an extension of the processing time, It is seen that in this mode generates the maximum amount of material to be removed for any focal decide to realize.
The foregoing considerations lead us to a first and important consequence:
- since the starting phase with the still spherical mirror, we will have the last diameter on the edge of the mirror, notoriously one that has a lower tolerance to defects in shape, is already “perfect mirror” and it will not be processed. It is already in “tolerance zone” and it is exactly in the center of the reference curves , because we have chosen to match the final parable and departure ball exactly in that diameter.
all the work of parabolizzazione will therefore be addressed to deepen the remaining internal areas to the edge in ascending order in hand to hand that we move towards the center.
METHOD “CENTRAL”
To conclude this small analysis , on the same basis we can say that the method A is what ( in our opinion ) less adapts to the process that we are studying as , like the method B It generates the maximum amount of material to be removed and, the point of tangency ( by definition the most “correct” ) on which we build the final figure, It is right in the center of the mirror, generally unused area.
ALL THAT WE NEED.
- the shiny mirror ball.
This step can be accomplished with standard techniques that we used for any other focal. There are no special precautions with respect to the normal processing, we can safely use the tool at full diameter ( indeed it is preferable ) and ran 1/3 COC to obtain the best possible ball.
Is’ well as from this stage to get used to work with the highest precision: The radius of curvature of our sphere must be accurately measured with the precision of at least 0,1 mm. The basic requirement that the starting sphere must have is that of being extremely correct in the peripheral zone.
As we have just seen, The edge with this method is the most important area, one on which we will build the whole parable, if it is a minimum tolerable defect on the central area which will then be excavated abundantly, it is not the last device area which will be processed very little, a minimum defect could be higher than the amount of material that must be removed making us impossible to reach the figure sought. So the bands of Ronchi will be absolutely straight up to the edge! - The tools in sub-diameter.
During the parabolizzazione of an F2-F4 , we can also forget about having a full tool diameter, or we use it more ( especially with the method to 100% ) until the next ball. What we're going to build will be three sub-diameter tools with patina modified “a stella” respectively 50% ( 40% in the case of perforated mirror ), 30% e 20% the diameter of the mirror. smaller tools may be useful in the final stages of small tweaks, but their use is always risky, the difficulty of processing and the probability of generating zonal defects increases with the decrease of the tool diameter, if we work carefully there is no need for additional tools. - The criteria.
We need to have a tester Ronchi e Foucault , which will accompany us until the 99% of these parable. The rest 1% It will be the most delicate and difficult part is how to process that as measures, Ronchi and Foucault have reached their limits and can no longer help , It will be necessary to have an apparatus to perform the caustic test, which should allow precise measures at least up to a hundredth of mm and with which we must necessarily have taken a little’ practice, maybe even using it in the pre-final stages of processing where it is not yet necessary. - The software for the analysis of the measures
There are many, but it is sufficient “Foucault Test Analysis” works , despite the name, It analyzes all three tests mentioned inter alia allowing the simulation of the Ronchi with the data of eddy readings and vice versa, very useful ! It is available in our download section.
- recklessness, luck and time available !
A mandatory warning to anyone reading these pages might decide to switch from simply reading the direct action: do not do it ! sconsigliatissimo is working hand-focal “extreme”, only the achievement of the parable“provisional” and not well corrected, could take months of work and the result is by no means certain, especially if you do not have a discrete practice with sub-diameter and a good relationship with the “Lady Luck”. The caustic tests requires a whole night for a measurement session and verification software, and in the last corrections may be required dozens of these tests.
And if you decide to try despite everything I can assure you, whatever happens, satisfaction guaranteed, It enters into an exciting and extreme world that will show you without veils the true essence of the processing of a mirror, a world where you will find many answers and new questions will be even more…
In the second part we will see how in practice we will start building our parable.